Sometimes people install Office onto a SQL Server to get the drivers for the ability to import data from Excel into SQL Server Tables. This should never be done on a production, or any, server because it can cause many other problems for SQL, one of which is the purpose of this blog.
For example, I had a client where every time the server or the SQL Engine was restarted things would look normal, but if a certain job ran the SQL Service would just stop (SEE BELOW IMAGE). Eventually, I figured out that if I ran the first step of the job in SSMS as Administrator it would continue to run successfully until the next restart. There were no errors in the SQL log that pointed to an obvious issue, and the client did not know why this was happening.
Come to find out that they had Office installed on their SQL Server and the job was importing an excel spreadsheet into a table which caused SQL to just STOP. The job ran an OPENROWSET query which had “Allow inprocess” set for the Linked Server Provider for Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.##.0. In order to load data into a table from an EXCEL spreadsheet via the OPENROWSET command, the linked server provider has to have “Allow inprocess” checked otherwise it won’t work. That setting along with the installation of Office causes SQL to just stop.
These conditions caused SQL to STOP the first time the job ran after a reboot. To get around this you would have to manually run the code first in SSMS as Administrator after each restart. Then from that point on, it would be fine until the next restart. It took time to figure out what exactly was causing this issue and it was due to Office being installed… specifically that Office needed elevated privileges that it did not have with the initial run. If you run the OPENROWSET in a query window without starting SSMS as Administrator, you can recreate this error every single time, as I was able to replicate the issue in my own testing environment. The error that you will see is as follows and SQL will just stop after the query, or likely, job starts.
Msg 109, Level 20, State 0, Line 0
A transport-level error has occurred when receiving results from the server. (provider: Shared Memory Provider, error: 0 - The pipe has been ended.)
Picture of SQL stopped in SQL Server Configuration Manager. This issue occurred regardless of the account that starts SQL – it did not matter if it was a local account or domain account.

I also saw this error in the SQL Logs. Adding the permissions in the registry did not fix this issue. It was set then it went away for some reason. This is due to Office being installed on the server.
UpdateUptimeRegKey: Operating system error 5(Access is denied.) encountered.Check to see if Office is installed and running on your server
There are a couple options to see if you have Office installed on your SQL Server. Some people just install Excel or a trial version of Office or the whole version of Office but either way it should not be installed on your SQL Server due to the possibility of SQL stopping randomly when a certain job that meets these requirements kicks off.
Option 1:
- Open Task Manager then click on the Details tab. You can add the Command line column if you want but look for “OfficeClicktoRun.exe”. If you see this, you have Office installed.
Examples:
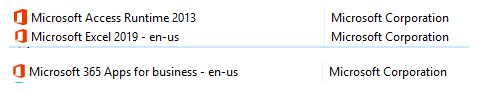
Instead of Office, we would only want the ODBC drivers installed.
Examples:
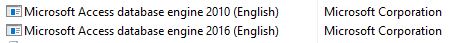
The FIX: Instructions using ODBC drivers to import Excel spreadsheet data into a table
If you already have a linked server for Excel, you do not need to create a new one.
- Uninstall Office.
- Download 64 bit or 32 bit ODBC driver, then install. You can install only one. In most instances, you need the 64-bit driver.
- Drivers can be found here – https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54920
- Create a linked server. No permissions are needed to be set for the location of the test server (i.e. c:\test) and no file is required to be there. In all actuality, the location doesn’t need to exist either, but you can create it anyway if you want.
- Replace C:\Test\test.xlsx with a location and filename as you choose.
- Replace ExcelServer with whatever name you want your Linked Server to be called.
- Replace Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0 with the ODBC version you plan on using. If you have multiple versions pick one since the linked server will be tied to that provider.
Example:
USE [master]
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_addlinkedserver @server = N'ExcelServer', @srvproduct=N'Excel', @provider=N'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0', @datasrc=N'C:\Test\test.xlsx', @provstr=N'Excel 12.0'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'collation compatible', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'data access', @optvalue=N'true'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'dist', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'pub', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'rpc', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'rpc out', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'sub', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'connect timeout', @optvalue=N'0'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'collation name', @optvalue=null
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'lazy schema validation', @optvalue=N'false'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'query timeout', @optvalue=N'0'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'use remote collation', @optvalue=N'true'
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_serveroption @server=N'ExcelServer', @optname=N'remote proc transaction promotion', @optvalue=N'true'
GO
4. Set SQL settings, run the following in a query window connected to the SQL Server.
Replace Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0 with the ODBC version you tied your linked server too (from above).
Exec sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
Exec sp_configure 'Ad Hoc Distributed Queries', 1;
RECONFIGURE;
GO
EXEC master.dbo.sp_MSset_oledb_prop N'Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0' , N'AllowInProcess' , 1;
GO
b. Verify the settings were set. Expand “Server Objects”, “Linked Servers”, “Providers”. Right click on the Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0 provider and click Properties.
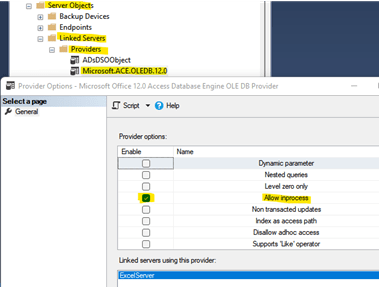
5. Reboot the server, not just the SQL Server services.Test your code in a query window. You don’t have to run both statements. I created examples of two ways to run an OPENROWSET insert statement.
Replace DB_Name with the database name you want to create the table in where the data is imported from the excel spreadsheet. The following are two different examples of code you can use.
Replace test and test2 with the table names you want to use. They must be different or just run one select statement.
Replace C:\import\test.xlsx with the location and excel spreadsheet filename.
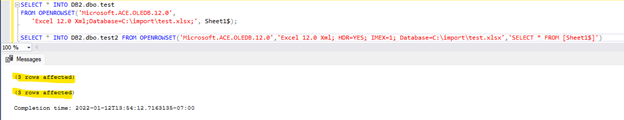
SELECT * INTO DB_name.dbo.test
FROM OPENROWSET('Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0',
'Excel 12.0 Xml;Database=C:\import\test.xlsx;', Sheet1$);
SELECT * INTO DB_name.dbo.test2 FROM OPENROWSET('Microsoft.ACE.OLEDB.12.0','Excel 12.0 Xml; HDR=YES; IMEX=1; Database=C:\import\test.xlsx','SELECT * FROM [Sheet1$]')
In conclusion, knowing what is installed on your SQL Servers is very important. If you are new to the environment, you should check all SQL settings, verify best practices, and verify what software is installed on the SQL servers you support, etc. Ensure MS Office or any component of MS Office is not installed on any SQL Server host, if it is uninstall Office and install just the ODBC drivers. Otherwise, you may have to deal with random stopping of SQL when a restart occurs if a process/job uses the above conditions.

